Important Factors for Choosing an RFID Antenna
When considering integrating an RFID system, it is crucial to take into account the technical specifications that RFID antennas must have. RFID antennas may appear quite similar at first glance, but this apparent uniformity is deceptive because it is in the technical details where these antennas truly differentiate themselves. The most important factors to consider are frequency, polarization, beam angle, and gain.
The frequency range indicates the radio wave spectrum in which the antenna can effectively operate. Gain and beam width, on the other hand, give us an idea of how far and how widely the antenna can transmit and receive signals. Lastly, polarization informs us about the orientation of the radio waves emitted by the antenna.
Understanding these parameters can help you select the antenna that best suits your needs and ensures the success of your RFID project. Thus, the depth and precision in analysing these technical specifications become a key factor in making an informed and accurate decision.
Types of Polarization for RFID Antennas
The polarization of an antenna refers to the direction in which the antenna emits and receives waves of energy. In the case of RFID antennas, there are primarily two types of polarization: linear and circular.
Linear Polarization
Linear polarization occurs when the electric field of an electromagnetic wave remains within the same plane during propagation. Antennas with linear polarization are ideal when RFID tags are consistently oriented relative to the antenna.
Linear polarization can be vertical or horizontal, depending on the orientation of the electric field. These antennas are simpler and tend to be cheaper compared to antennas with circular polarization.
The major benefit of linear polarization antennas is that they offer a greater reading range compared to circular polarization antennas when the RFID tags are correctly aligned. However, their main disadvantage is that if the RFID tag moves or is oriented differently, the reading performance can be significantly affected.
Linear polarization antennas are common in applications where the tag orientation is known and constant, such as in manufacturing tracking systems or assembly lines.
Circular Polarization
Circular polarization, on the other hand, occurs when the electric field of the electromagnetic wave rotates in a circular pattern as the wave propagates. Antennas with circular polarization are preferred when RFID tags change orientation or position relative to the antenna.
The main advantage of circular polarization antennas is that they provide more consistent reading of RFID tags, regardless of their orientation or position. However, they often have a shorter reading range than linear polarization antennas and are usually more expensive.
Circular polarization antennas can be right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) or left-hand circular polarization (LHCP), and they are more complex in construction than linear polarization antennas.
- Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP): In an RHCP wave, if you are looking in the direction of wave propagation, the electric field rotates clockwise.
- Left-Hand Circular Polarization (LHCP): Conversely, in an LHCP wave, the electric field rotates counterclockwise when viewed in the direction of wave propagation.
Circular polarization antennas are ideal for applications where the orientation of RFID tags can vary, such as tracking goods in a warehouse, access control systems, or marathon races, where they are used to tracking runners.
The choice between linear and circular polarization largely depends on the specific application and the conditions in which the RFID system will be used. Therefore, it is important to consider these factors when choosing the type of polarization for an RFID system.

Frequencies of Antennas
As we have explained in other articles, it is essential to determine the frequency required for our RFID system. Understanding the different RFID frequencies and how they interact with different materials and environments is crucial in choosing the right RFID antenna for your specific system and application.
- UHF Antennas: Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID antennas operate in ranges that vary between 860-960 MHz, depending on country regulations. UHF antennas can have reading ranges of up to 12 meters or more, making them ideal for inventory tracking, supply chain management, long-range vehicle access control, and sports timing applications. However, they are more susceptible to interference from liquids and metals.
- HF Antennas: High-Frequency (HF) RFID antennas operate in the 13.56 MHz band. They have a reading range that can reach up to one meter. Like LF antennas, HF antennas are relatively immune to environmental interference. Common applications for HF antennas include document management, libraries, and contactless payment systems.
- LF Antennas: Low-Frequency (LF) RFID antennas operate in a frequency range of 125 to 134.2 kHz. These antennas are suitable for short-range applications, typically less than half a meter, and are less susceptible to interference from metals or liquids. This makes them suitable for applications such as animal tracking, access control, or vehicle identification.
Antenna Gain and Beam Width
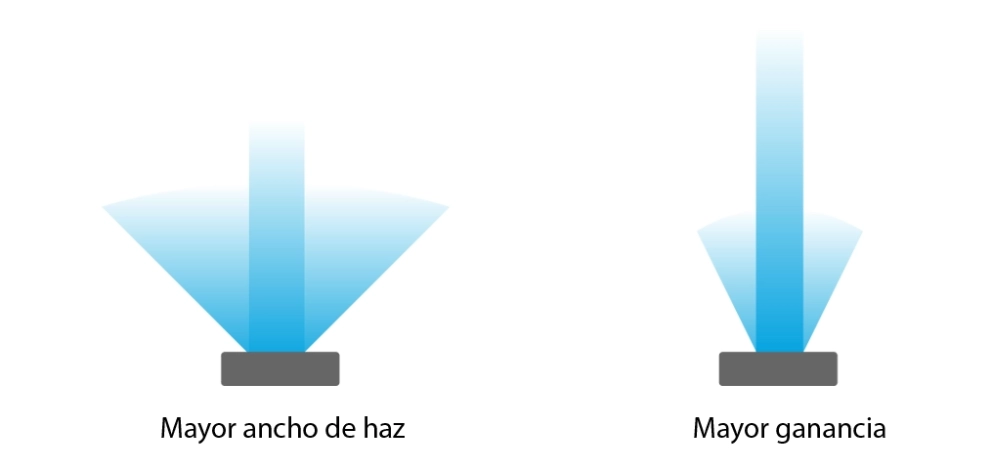
Antenna gain and beam width are two related attributes of an antenna. Higher gain results in a narrower beam width, and conversely, lower gain leads to a wider beam width.
Antenna gain refers to its ability to concentrate radiofrequency energy in a specific direction, increasing the signal intensity in that direction. Gain is measured in decibels isotropic (dBi). Beam width, also known as beam angle or beamwidth, represents the coverage breadth that an RFID antenna can provide. This factor directly affects the area in which RFID tags can be read and written.
If the beam width is wide, the antenna will provide broader coverage, enabling the reading and writing of tags in an extensive area. However, a wide beam width may carry a higher risk of interference, which can compromise the accuracy of tag reading. On the other hand, a narrower beam width can provide higher reading precision but limits the coverage area.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an RFID Antenna
The selection of the antenna type and its polarization is crucial for the effective operation of an RFID system. Below are some key factors to consider when making this choice.
- Operating Environment: Environmental conditions can significantly influence the antenna selection. For example, in environments with high humidity or the presence of metals, a specific antenna with certain characteristics may be required to ensure optimal performance.
- Tag Orientation: As mentioned earlier, the orientation and movement of RFID tags can influence the choice of polarization. If the tags are consistently oriented, linear polarization may be the most efficient option. On the other hand, if the tags change orientation or position relative to the antenna, circular polarization would be the better choice.
- Required Reading Range: The distance at which the RFID tags need to be read will also influence the type of antenna chosen. Some antennas, such as UHF antennas, can read at longer distances, while others, such as LF and HF antennas, are more suitable for short-range readings.
- Cost: Cost can also be a deciding factor. Depending on the available budget, it may be more appropriate to choose one type of antenna or polarization over another.
- Local Regulations: Local regulations and standards can limit the types of antennas and frequency bands that can be used, so it is essential to verify these regulations before selecting an antenna.
Other Factors to Consider for RFID Antennas
In addition to polarization, gain, and frequency, there are other aspects that can influence the performance of an RFID system. Among them, antenna size is a crucial factor. The physical dimensions of an antenna will dictate the installation space available. We may have an antenna that is perfect for our needs, but if its size or thickness prevents it from being installed in the desired location, it may not be suitable.
Regarding environmental protection, it is important to consider the conditions in which the antenna will operate. For example, if it will be installed outdoors, the antenna should be waterproof and UV-resistant to avoid damage from rain or sun exposure. Similarly, if it will be used in an industrial environment, it may need to withstand dust, grease, or vibrations. Therefore, choosing an antenna with the appropriate level of environmental protection is essential to ensure its long-term durability and reliability.
Finally, the type of connection is another important factor, as RFID antennas can be connected to the RFID reader using different types of connections. The choice of connection type will depend largely on the specific needs of the installation and system. Wired connections, such as coaxial connections, typically provide high-quality signal transmission, but we must consider what type of connector it has to ensure proper functioning of our RFID antennas.
Related products
Contact Form
We can help you?
Find the RFID product or solution that meets your business needs.
Ask us to help you find the right decision.



